产品组成
| 货号 |
CLODRONATE SUV PEG LIPOSOMES |
CONTROL SUV PEG LIPOSOMES |
| C419764-2×5ml |
C419508-5ml |
C419763-5ml |
| C419764-2×10ml |
C419508-10ml |
C419763-10ml |
| C419764-2×15ml |
C419508-15ml |
C419763-15ml |
| C419764-2×20ml |
C419508-20ml |
C419763-20ml |
| C419764-2×30ml |
C419508-30ml |
C419763-30ml |
| C419764-2×40ml |
C419508-40ml |
C419763-40ml |
| C419764-2×50ml |
C419508-50ml |
C419763-50ml |
|
产品描述
氯膦酸钠SUV-PEG脂质体
人工球体由单个磷脂双层组成,包裹含有氯膦酸盐的PBS(磷酸盐缓冲盐水)水溶液。将含有脂质的特殊PEG添加到组合物中,允许血液中长时间循环,并减缓制剂的降解。脂质体悬浮液已挤出,直径为200纳米,储存时不会沉淀。悬浮液中氯膦酸盐的浓度约为5 mg/ml。
根据要求,可以通过额外的挤压步骤将尺寸减小到120-150nm。
对照SUV-PEG脂质体
对照脂质体不含氯膦酸盐。仅含PBS,可用于对照实验,以确定注射氯膦酸盐脂质体后观察到的效应是否完全是由于巨噬细胞耗竭所致。脂质体分散体是用一种特殊的含有脂质的PEG制备的,这种脂质可以在血液中长时间循环,减缓制剂的降解。该制剂已被挤出,直径为200nm,这使其成为氯膦酸钠SUV-PEG脂质体的首选对照品。
根据要求,可以通过额外的挤压步骤将尺寸减小到120-150nm。
储存和使用说明
给药前,先让脂质体达到室温,轻轻摇晃或搅拌混悬液。脂质体往往会在一段时间后沉淀,导致小瓶中分布不均匀。当注射时间过长时,脂质体甚至可能在注射器中沉淀。如果使用同一个注射器注射多只动物,这可能会导致剂量不同。
不鼓励稀释悬浮液,但如有必要,请使用 PBS 或盐水。
我们建议客户在发货后 16 周内使用我们的脂质体制剂。强烈建议不要在到期日之后使用。在这段时间之后,污染的风险会增加,并且可能会发生轻微的功能丧失。
作用机制
巨噬细胞在免疫和非免疫防御机制中发挥重要作用。它们构成了抵御细菌、病毒和其他形式的微生物污染侵入脊椎动物体内的第一道防线。巨噬细胞是大细胞,几乎存在于所有身体组织中,它们可以有不同的形式和名称(例如,枯否细胞、肺泡巨噬细胞、小胶质细胞、破骨细胞、红髓巨噬细胞)。巨噬细胞“清除”,它们摄取和消化所有可能是潜在病原体的外来物质、微生物、癌细胞和细胞碎片。这个过程称为吞噬作用。巨噬细胞进一步调节许多非吞噬细胞的功能,主要是通过介导可溶性分子如细胞因子和趋化因子。它们参与先天免疫。
脂质体是人工制备的球体,由同心磷脂双层组成。当磷脂分散在水中时,亲水性头部将构成脂质体的两个外部部分,而疏水性脂肪酸基团将构成内部部分(见图 1)。水性隔室将双层隔开,亲水性分子可以溶解在其中,从而产生脂质体包裹的分子。氯膦酸盐(二氯亚甲基二膦酸盐或 Cl2MBP)是一种亲水分子,可以封装在磷脂双层中。游离的氯膦酸盐不易穿过细胞膜,并被肾系统从循环中迅速清除(即在几分钟内)。然而,当包裹在脂质体中时,氯膦酸盐脂质体会被巨噬细胞摄取而无法逃脱(见图 2)。磷脂双分子层被溶酶体磷脂酶消化,而氯膦酸盐不被消化并保留在巨噬细胞中。巨噬细胞摄入的磷脂双分子层和脂质体越多,氯膦酸盐就会在巨噬细胞内积累越多。超过一定的细胞内浓度,氯膦酸盐将通过启动其程序性细胞死亡,即细胞凋亡来消除巨噬细胞。
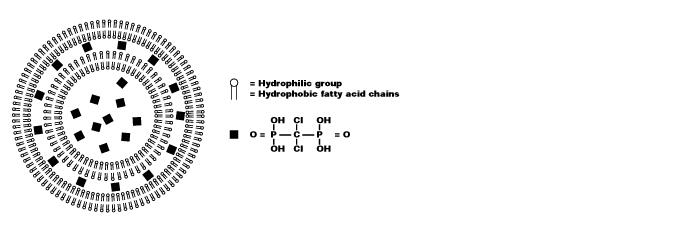
图 1. 氯膦酸盐脂质体的示意图。囊泡由同心磷脂双层组成,由水性隔室隔开。双层由亲水和疏水基团组成。氯膦酸盐(此处以黑色方块表示)溶解在水溶液中并封装在脂质体中。
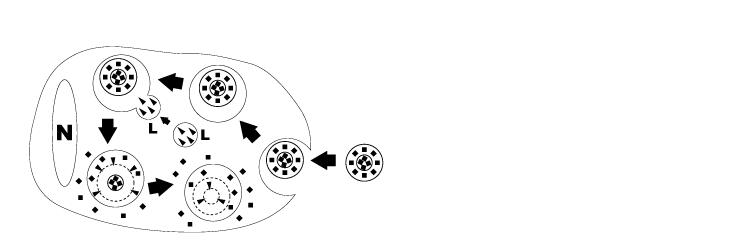
图 2. 巨噬细胞摄取和消化氯膦酸盐脂质体的示意图。氯膦酸盐脂质体通过内吞作用被巨噬细胞摄取,然后与含有磷脂酶的溶酶体 (L) 融合(箭头)。磷脂酶破坏的磷脂双分子层越多,巨噬细胞内释放的氯膦酸盐(黑色方块)就越多。巨噬细胞最终通过凋亡被杀死。(N = 巨噬细胞核)。
因此,氯膦酸盐脂质体可用于通过消耗巨噬细胞来研究巨噬细胞的功能。例如,它们可以应用于各种自身免疫疾病、移植、神经系统疾病和基因治疗的模型。氯膦酸盐脂质体只有在可以达到的情况下才能消耗巨噬细胞。一些组织可以形成脂质体的屏障。通过选择氯膦酸盐脂质体的正确给药途径,可以耗尽特定器官或组织的巨噬细胞。
PBS 脂质体主要用于对照实验。然而,这些也可以通过饱和来阻止吞噬作用一段时间。因此,PBS 脂质体不代表正常健康、非阻塞、非抑制和非活化巨噬细胞的对照实验。当比较氯膦酸盐脂质体与 PBS 脂质体的效果时,效果可能低于预期。
PRODUCT COMPOSITION
| 货号 |
CLODRONATE SUV PEG LIPOSOMES |
CONTROL SUV PEG LIPOSOMES |
| C419764-2×5ml |
C419508-5ml |
C419763-5ml |
| C419764-2×10ml |
C419508-10ml |
C419763-10ml |
| C419764-2×15ml |
C419508-15ml |
C419763-15ml |
| C419764-2×20ml |
C419508-20ml |
C419763-20ml |
| C419764-2×30ml |
C419508-30ml |
C419763-30ml |
| C419764-2×40ml |
C419508-40ml |
C419763-40ml |
| C419764-2×50ml |
C419508-50ml |
C419763-50ml |
|
DESCRIPTION
Clodronate SUV PEG Liposomes
Artificial spheres consisting of a single phospholipid bilayer encapsulating an aqueous PBS (phosphate buffered saline) solution containing clodronate. A special PEG-containing lipid is added to the composition, which allows for long circulation in blood and slower degradation of the formulation. The Liposomal suspension has been extruded and sized to 200nm in diameter and will not tend to precipitate upon storage. The concentration of clodronate in the suspension is ca. 5 mg/ml.
Upon request, the size can be reduced to 120-150nm with an extra extrusion step.
Control SUV PEG Liposomes
Control liposomes do not contain clodronate. Containing PBS only, they can be used for control experiments, in order to find out whether the effects observed after injection of clodronate liposomes are due to macrophage depletion exclusively. The Liposomal dispersion has been prepared with a special PEG-containing lipid which allows for long circulation in blood and slower degradation of the formulation. This formulation has been extruded and sized to 200nm in diameter which makes it the preferred control for the Clodronate SUV PEG liposomes.
Upon request, the size can be reduced to 120-150nm with an extra extrusion step.
STORAGE AND DIRECTIONS OF USE
Upon arrival, liposomes should be stored between 4 – 8 ºC (or 39 – 47 ºF). The liposomal suspensions should never be frozen, nor be exposed to extreme high temperatures. This can cause disturbances to the phospholipid bilayers, possibly leading to leakage of clodronate out of the liposome.
Before administration, let the liposomes reach room temperature first and gently shake or stir the suspension. Liposomes tend to precipitate after some time, causing an inhomogeneous distribution in the vial. When injection takes too much time, the liposomes may even precipitate in the syringe. If multiple animals are injected using the same syringe, this can cause differential dosing.
Dilution of the suspension is discouraged, but if necessary use PBS or saline.
We advise our customers to use our liposomal formulation within 16 weeks after shipment. Use after the expiry date has occurred is strongly discouraged. After this period the risk of contamination increases, and a slight loss of function could occur.
MECHANISM OF ACTION
Macrophages play an important role in immune and non-immune defence mechanisms. They form a first line of defence against bacterial, viral and other forms of microbiological contamination penetrating into the bodies of vertebrates. Macrophages are large cells, found in almost all bodily tissues where they can have varying forms and names (e.g. Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, osteoclasts, red pulp macrophages). Macrophages “scavenge”, they ingest and digest all foreign substances, microbes, cancer cells and cellular debris that might be potential pathogens. This process is called phagocytosis. Macrophages further regulate functions of many non-phagocytic cells, mainly through mediation of soluble molecules such as cytokines and chemokines. They are involved in innate immunity, adaptive immunity and can have (anti-) inflammatory effects.
Liposomes are artificially prepared spheres and consist of concentric phospholipid bilayers. When phospholipids are dispersed in water, the hydrophilic heads will make up both outer parts of the liposome, whereas the hydrophobic fatty acid groups will make up the inner part (see figure 1). Aqueous compartments separate the bilayers, and hydrophilic molecules can be dissolved in it, resulting in liposome-encapsulated molecules. Clodronate (dichloromethylene-bisphosphonate or Cl2MBP) is a hydrophilic molecule that can be encapsulated within phospholipid bilayers. Free clodronate does not easily cross cell membranes, and is rapidly cleared (i.e. within minutes) from circulation by the renal system. However, when entrapped in a liposome, the clodronate liposome is ingested by macrophages and cannot escape it (see figure 2). The phospholipid bilayers are digested by lysosomal phospholipases, whereas clodronate is not digested and remains in the macrophage. The more phospholipid bilayers and liposomes are ingested by the macrophage, the more clodronate will accumulate within the macrophage. Exceeding a certain intracellular concentration, clodronate will eliminate the macrophage by initiating its programmed cell death, i.e. apoptosis.
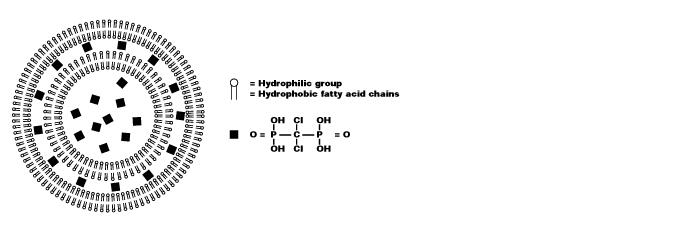
Figure 1. Schematic representation of a clodronate liposome. The vesicle consists of concentric phospholipid bilayers, separated by aqueous compartments. The bilayers consist of a hydrophilic and hydrophobic group. Clodronate (represented here as black squares) are dissolved in the aqueous solution and encapsulated within the liposome.
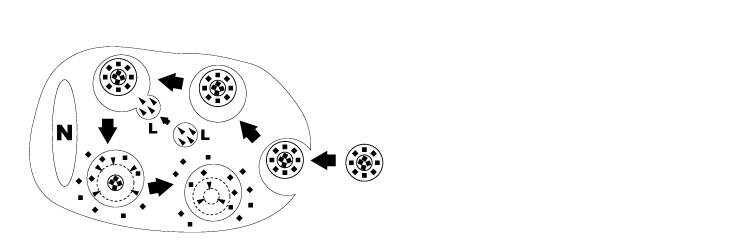
Figure 2. Schematic representation of clodronate liposome ingestion and digestion by a macrophage. Clodronate liposomes are ingested by the macrophages via endocytosis and then fused with the lysosomes (L) which contain phospholipases (arrowheads). The more phospholipid bilayers are disrupted by the phospholipases, the more clodronate (black squares) is released within the macrophage. Macrophages are ultimately killed through apoptosis. (N = nucleus of macrophage).
Thus, clodronate liposomes can be used to study macrophage functioning by depletion of macrophages. For instance, they can be applied in various models of autoimmune disease, transplantation, neurological disorders and gene therapy. Clodronate liposomes are only able to deplete macrophages if they can be reached. Some tissues can form barriers for the liposomes. By choosing the right administration route of clodronate liposomes, particular organs or tissues can be depleted of macrophages.
PBS liposomes are mostly used for control experiments. However, these too can block phagocytosis by saturation for certain periods of time. PBS liposomes thus do not represent a control experiment with normal healthy, non-blocked, non-suppressed and non-activated macrophages. When comparing effects of clodronate liposomes with PBS liposomes, the effects can therefore be less than expected.
ADMINISTRATION PROTOCOLS
Administration protocols should be chosen carefully and depend on several factors, for instance: the type of macrophage you intend to deplete (e.g. Kupffer cells, alveolar macrophages, microglia, osteoclasts, red pulp macrophages), the time in which you intend to maintain depletion (e.g. short or long term), the (animal) model, and other experimental factors. In vitro application of clodronate liposomes is possible, albeit that they are specifically suitable to study macrophages in vivo. Below you can see schematic representations of the tissues and macrophages that can be reached through different administration routes. Please note that not all tissues and routes are represented here.
Abbreviations: AL = lung alveoli, BM = bone marrow, BR = brain, BV = blood vessels / circulation, DA = draining area of lymph node, EY = eye, GU = gut / intestines, IV = intravenous delivery, KI = kidney, LI = liver, LN = lymph node, LU = lung, LV = lymph vessels, PE = peritoneal cavity, SP = spleen, SY = synovial cavity in joint, TE = testis, TR = trachea.
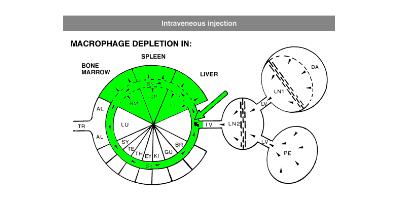
In general, it is recommend to inject 100 µL of suspension / 10 grams of animal weight for intravenous injection. Raising the dosage considerably may lead to blockage of capillaries. Intravenous administration of clodronate liposomes will lead to maximum depletion of liver and spleen macrophages in ca. 24 hours. Dependent on the subset of macrophages they will remain depleted for ca. 5 days. After that time, new macrophages will replace the depleted ones: macrophage precursors, monocytes, that are formed in bone marrow and released in circulation will arrive at their destination and further differentiate into mature macrophages. Monocytes,macrophage precursors, can also be depleted. To prevent macrophage repopulation, multiple injections can be administered every 2-3 days to target monocytes. See for instance: Sunderkötter, C., Nikolic, T., Dillon, M. J., Van Rooijen, N., Stehling, M., Drevets, D. A., & Leenen, P. J. (2004). Subpopulations of mouse blood monocytes differ in maturation stage and inflammatory response. The Journal of Immunology, 172(7), 4410-4417.
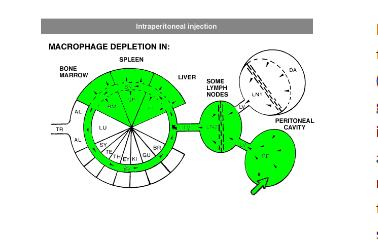
For intraperitoneal administration, the recommended injection dosis (i.e. 100 µL of suspension / 10 grams of animal weight) can be increased considerably. This route also depletes peritoneal macrophages, but will take longer to deplete macrophages in liver and spleen (ca. 3 days). Depletion is slower and more gradual, since the liposomes have to be carried from the peritoneal cavity to circulation by lymph flow via the thoracic duct, which is a passive form of transport.
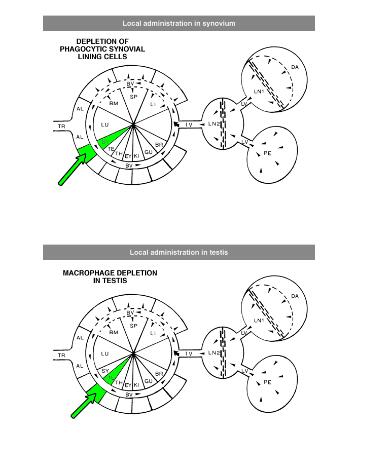
Local administration is often required to target macrophages that are difficult to reach, such as macrophages in testis or the phagocytic synovial lining cells.
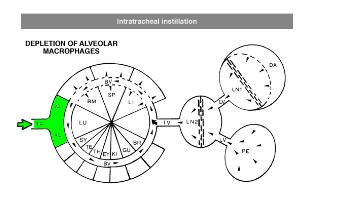
For depletion of alveolar macrophages, clodronate liposomes can be administered intranasally as well as intratracheally. The difference is that intranasal liposomes may be spoiled in the oesophagus if not administered properly, whereas intratracheal instillation will deliver all liposomes in the lung. Please note that these routes only target alveolar macrophages, and not interstitial macrophages. These can be targeted through depletion of blood monocytes in circulation. See for instance: Huang, L., Nazarova, E. V., Tan, S., Liu, Y., & Russell, D. G. (2018). Growth of Mycobacterium tuberculosis in vivo segregates with host macrophage metabolism and ontogeny. Journalof Experimental Medicine, 215(4), 1135-1152.
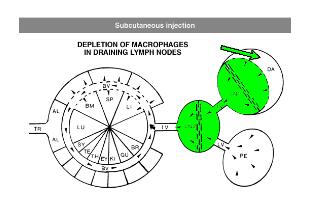
For subcutaneous injection the maximum volume to be injected depends on the storage capacity of the injection site.
RESULTS
Sections of mouse liver, stained with monoclonal antibody F4/80 Normal liver with positive Kupffer cells.
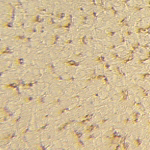
Liver of a mouse, 2 days after injection with clodronate-liposomes. Kupffer cells have been depleted

Sections of mouse spleen stained for acid phosphatase Normal spleen with positive splenic macrophages

Spleen of a mouse 2 days after injection with clodronate liposomes. Only few macrophages are left














