Reductive Alkylation Kit-Hampton 还原烷基化试剂盒
上海金畔生物代理Hampton research品牌蛋白结晶试剂耗材工具等,我们将竭诚为您服务,欢迎访问Hampton research官网或者咨询我们获取更多相关Hampton research品牌产品信息。


Products > Optimization Screens > Reductive Alkylation > Reductive Alkylation Kit
Reductive Alkylation Kit
Applications
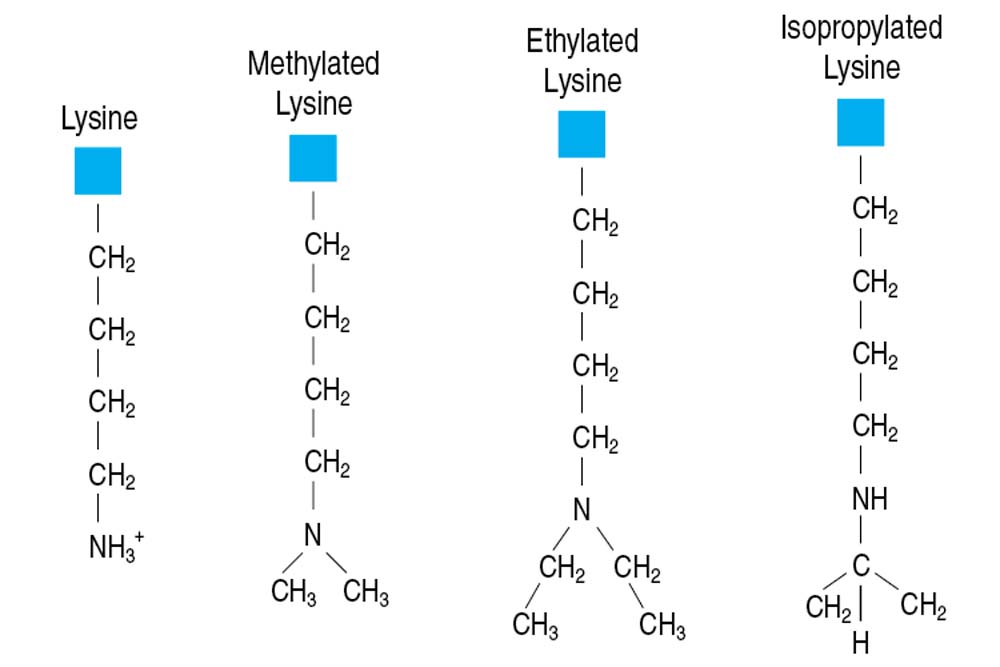
- Reductive alkylation of lysine residues to change protein properties (pI, solubility and hydropathy) which may promote crystallization via improved crystal packing.
Features
- Flexible protocol allows for methylation or ethylation or isopropylation of lysine
- 6 Reductive alkylation reactions
- A surface-engineered protein, ready for crystallization, is produced within 24 hours
- Optimized protocol for selective alkylation of lysine residues
- Methanol free formaldehyde
- Can be used to manipulate sample solubility and pI
Description
The Reductive Alkylation Kit offers a flexible alkylation protocol for methylation or ethylation or isopropylation of lysine residues.
Reductive alkylation of lysine residues to change protein properties (pI, solubility and hydropathy) which may promote crystallization via improved crystal packing.
Reductive alkylation of proteins has been successfully applied to obtain a significant number of high-quality crystals from proteins previously unable to be crystallized. Alkylating the e amino group of lysines alters the hydropathy, solubility and pI of the protein which may promote crystallization by altering sample-sample, sample-solvent and crystal packing interactions.
Reductive alkylation does not change the intrinsic charge on a protein but may change the isoelectric point (pI) slightly. The N-terminal amino group on the backbone will also be reductively alkylated. In general, alkylated proteins retain their original biochemical function. This protocol is designed with the goal of generating a high degree of modification with few side reactions, resulting in a homogeneous population of protein.
赖氨酸残基的还原烷基化以改变蛋白质特性(pI、溶解度和亲水性),这可能通过改进的晶体堆积促进结晶。
特征
灵活的方案允许赖氨酸的甲基化、乙基化或异丙基化
6 还原性烷基化反应
可在 24 小时内生产出可用于结晶的表面工程蛋白
赖氨酸残基选择性烷基化的优化方案
无甲醇甲醛
可用于控制样品溶解度和 pI
描述
还原性烷基化试剂盒为赖氨酸残基的甲基化、乙基化或异丙基化提供了灵活的烷基化方案。赖氨酸残基的还原烷基化以改变蛋白质特性(pI、溶解度和亲水性),这可能通过改进的晶体堆积促进结晶。蛋白质的还原烷基化已成功应用于从以前无法结晶的蛋白质中获得大量高质量晶体。将赖氨酸的 e 氨基烷基化会改变蛋白质的亲水性、溶解性和 pI,这可能通过改变样品-样品、样品-溶剂和晶体堆积相互作用来促进结晶。
还原性烷基化不会改变蛋白质的固有电荷,但可能会略微改变等电点 (pI)。主链上的 N 端氨基也将被还原性烷基化。通常,烷基化蛋白质保留其原始的生化功能。该协议的设计目标是产生高度修饰,几乎没有副反应,从而产生均匀的蛋白质群。
HR2-434 Reductive Alkylation Kit

CAT NO
HR2-434
NAME
DESCRIPTION
tube format
PRICE
$298.00
cart quote
Support Material(s)
 HR2-434 Reductive Alkylation Kit User Guide
HR2-434 Reductive Alkylation Kit User Guide HR2-434 Reductive Alkylation Kit SDS
HR2-434 Reductive Alkylation Kit SDSReferences
1. Large-scale evaluation of protein reductive methylation for improving protein crystallization. Kim et al. Nature Methods, Volume 5, Number 10, page 853-854, October 2008.
2. Lysine methylation as a routine rescue strategy for protein crystallization. Walter et al. Structure 14, 1617-1622, November 2006.
3. A pivotal role for reductive methylation in the de novo crystallization of a ternary complex composed of Yersinia pestis virulence factors YopN, SycN and YscB. Florian D. Schubot and David S.Waugh. Acta Cryst. (2004). D60, 1981-1986.
4. Reductive alkylation of lysine residues to alter crystallization properties of proteins. Ivan Rayment. Methods in Enzymology, Volume 276, 171-179, (1997).
5. Crystallization and improvement of crystal quality for X-ray diffraction of maltooligosyl trehalose synthase by reductive methylation of lysine residues. Matsuura et al. Acta Cryst. (1999). D55, 931-933.
6. Structural consequences of reductive methylation of lysine residues in hen egg white lysozyme: An X-ray analysis at 1.8 angstrom resolution. Rypniewski, W.R., Holden, H.M., and Rayment, I. (1993). Biochemistry 32, 9851-9858.
7. Reductive alkylation of amino groups in proteins. Means, G. E. & Feeney, R. E. (1968). Biochemistry, 7, 2192-2201.
8. Double chromodomains cooperate to recognize the methylated histone H3 tail. Flanagan et al. Nature, 438, 1181-1185 (2005).
9. Reductive Isopropylation of Amino Groups in Lysine Containing Peptides. Brown and Greenberg. Analytical Letters, Volume 17, Issue 12 1984 , pages 1429-1445.
10. Selectivity in the Modification of the a-Amino Groups of Hemoglobin on Reductive Alkylation with Aliphatic Carbonyl Compounds. Acharya et al. Journal of Biological Chemistry, Vol. 260, No. 10, Issue of May 25, pp. 6039-6046, 1985.
11. Accessibility and mobility of lysine residues in beta-lactoglobulin. Brown et al. Biochemistry, 1988, 5601-5610.
