TCEP hydrochloride-Hampton TCEP盐酸盐
上海金畔生物代理Hampton research品牌蛋白结晶试剂耗材工具等,我们将竭诚为您服务,欢迎访问Hampton research官网或者咨询我们获取更多相关Hampton research品牌产品信息。


Products > Optimize Reagents > Optimize – Reducing Agent > TCEP hydrochloride
TCEP hydrochloride
Applications
- Stable reducing agent for crystallization trials
Features
- Highly soluble
- Odorless and non-volatile
- Effective at acidic and alkaline pH
Description
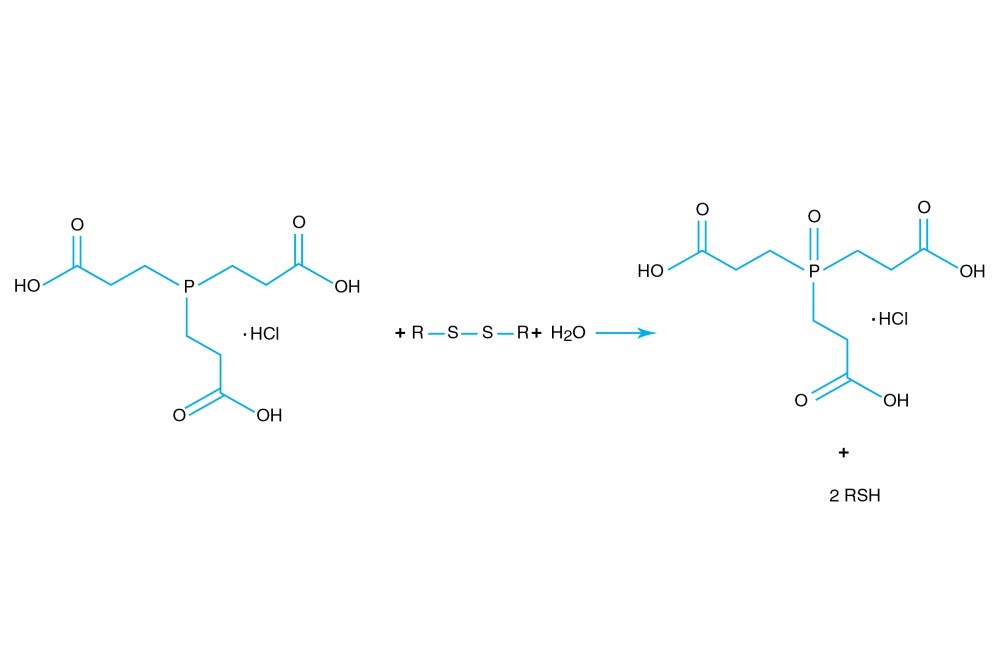
TCEP hydrochloride is Tri(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine hydro-chloride.
TCEP hydrochloride is an odorless, non-volatile reducing agent that is more stable and effective than DTT or 2-Mercaptoethanol. Unlike DTT, TCEP hydrochloride retains its reducing power at acid pHs (pH 5) and at pHs above 7.5 and is stable in air. TCEP hydrochloride is soluble in water to 310 grams per liter. For most applications, 5-50 mM TCEP provides sufficient molar excess to effectively reduce peptide or protein disulfide bonds within a few minutes at room temperature. TCEP hydrochloride is unreactive toward other functional groups found in proteins. Unlike DTT (dithiothreitol), TCEP hydrochloride does not contain a free thiol, and therefore does not require removal before reaction with thiol-reactive reagents. TCEP reduces disulfides but apparently not mercury-thiol bonds. TCEP hydrochloride is compatible with many heavy atoms and may be used during heavy atom derivatization. TCEP hydrochloride is more stable at a higher pH and at higher temperatures than is DTT and for a longer period of time in buffers without metal chelators such as EGTA. With TCEP, removal of the reducing agent is not necessary prior to most applications, (e.g. histidine-tagged protein purification, protein crystallization).
TCEP is typically very soluble in aqueous buffers at nearly any pH. Therefore, working concentrations and 10X stock solutions may be readily prepared in most aqueous buffers. TCEP is stable in aqueous, acidic, and basic solutions. When TCEP is dissolved directly in water, the resulting pH is approximately 2.5. TCEP is not very stable in phosphate buffers, especially at neutral pH. Therefore, if TCEP is to be used in PBS buffers, prepare the working solution immediately before use. TCEP may be used as a substitute loading buffer for SDS-PAGE; use a final concentration of 50 mM TCEP. Since TCEP is charged in solution, it is not compatible for use in isoelectric focusing.
A 10 mM TCEP hydrochloride concentration can reduce the pH of a 100 mM buffer by approximately 0.5 pH units; 1 mM TCEP hydrochloride concentration reducing the pH of a 100 mM buffer by 0.05 pH units.
Stability in Solution
TCEP is stable in aqueous acidic and basic solutions. When TCEP is dissolved directly in water the resulting pH is 2.5. Various buffers may be used for the reductions. Studies indicate that no change in concentration occurs after 24 hour incubation at room temperature in 100 mM HCL, 100 mM NaOH, or any of the following 50 mM buffers Tris HCl (pH 7.5, 8.5, 9.5), HEPES(pH 6.8, 8.2), Borate(pH 8.2, 10.2), and CAPS (pH 9.7, 11.1). Even after weeks in these buffers, less than 20% of the TCEP was oxidized.
TCEP is not particularly stable in phosphate buffers, especially at neutral pH. Experiments indicate that TCEP completely oxidizes within 72 hours in 0.35M phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), pH 7.0. Approximately 50% oxidation occurs in the same amount of time in 0.15M PBS, pH 8.0. Only minimal oxidation occurs in PBS at pH > 10.5 or < 6.0. Therefore, if TCEP is to be used in PBS buffers, prepare the working solution immediately before use.
Solid TCEP hydrochloride is supplied packaged in argon to minimize oxidation.
Molecular formula C9H15O6P • HCl
Molecular weight 286.65
CAS [51805-45-9]
Beilstein Registry Number 3724376
Purity ≥99.0%
Stable at room temperature for up to 2 years after receipt.
TCEP盐酸盐
应用
用于结晶试验的稳定还原剂
特征
高度溶解
无味且不挥发
在酸性和碱性 pH 值下有效
描述
TCEP盐酸盐是三(2-羧乙基)膦盐酸盐。
TCEP 盐酸盐是一种无味、不挥发的还原剂,比 DTT 或 2-巯基乙醇更稳定、更有效。与 DTT 不同,TCEP 盐酸盐在酸性 pH 值 (pH 5) 和高于 7.5 的 pH 值下保持其还原能力,并且在空气中稳定。 TCEP盐酸盐溶于水至每升310克。对于大多数应用,5-50 mM TCEP 提供足够的摩尔过量,以在室温下几分钟内有效地减少肽或蛋白质二硫键。 TCEP 盐酸盐对蛋白质中发现的其他官能团没有反应。与 DTT(二硫苏糖醇)不同,TCEP 盐酸盐不含游离硫醇,因此在与硫醇反应试剂反应之前不需要去除。 TCEP 减少二硫化物,但显然不能减少汞-硫醇键。 TCEP 盐酸盐与许多重原子相容,可用于重原子衍生化。与 DTT 相比,TCEP 盐酸盐在更高的 pH 值和更高的温度下更稳定,并且在不含金属螯合剂(如 EGTA)的缓冲液中更稳定。使用 TCEP,在大多数应用(例如组氨酸标记的蛋白质纯化、蛋白质结晶)之前不需要去除还原剂。
TCEP 通常在几乎任何 pH 值的水性缓冲液中都非常易溶。因此,可以在大多数水性缓冲液中轻松制备工作浓度和 10X 储备溶液。 TCEP 在水溶液、酸性和碱性溶液中稳定。当 TCEP 直接溶解在水中时,所得的 pH 值约为 2.5。 TCEP 在磷酸盐缓冲液中不是很稳定,尤其是在中性 pH 值下。因此,如果要在 PBS 缓冲液中使用 TCEP,请在使用前立即准备工作溶液。 TCEP 可用作 SDS-PAGE 的替代加载缓冲液;使用终浓度为 50 mM 的 TCEP。由于 TCEP 在溶液中带电,因此不适用于等电聚焦。
10 mM TCEP 盐酸盐浓度可使 100 mM 缓冲液的 pH 值降低约 0.5 个 pH 单位; 1 mM TCEP 盐酸盐浓度将 100 mM 缓冲液的 pH 值降低 0.05 个 pH 单位。
溶液稳定性
TCEP 在酸性和碱性水溶液中稳定。当 TCEP 直接溶解在水中时,所得的 pH 值为 2.5。各种缓冲器可用于减少。研究表明,在室温下在 100 mM HCL、100 mM NaOH 或任何以下 50 mM 缓冲液 Tris HCl(pH 7.5、8.5、9.5)、HEPES(pH 6.8、8.2)中孵育 24 小时后,浓度不会发生变化、硼酸盐(pH 8.2、10.2)和CAPS(pH 9.7、11.1)。即使在这些缓冲液中放置数周后,也只有不到 20% 的 TCEP 被氧化。
TCEP 在磷酸盐缓冲液中不是特别稳定,尤其是在中性 pH 值下。实验表明,TCEP 在 pH 7.0 的 0.35M 磷酸盐缓冲盐水 (PBS) 中的 72 小时内完全氧化。在 0.15M PBS,pH 8.0 中,大约 50% 的氧化在相同的时间内发生。在 pH > 10.5 或 < 6.0 的 PBS 中仅发生最小的氧化。因此,如果要在 PBS 缓冲液中使用 TCEP,请在使用前立即准备工作溶液。
固体 TCEP 盐酸盐以氩气包装提供,以最大程度地减少氧化。
分子式 C9H15O6P • HCl
分子量 286.65
中国科学院 [51805-45-9]
贝尔斯坦注册号 3724376
纯度≥99.0%
收到后在室温下可稳定长达 2 年。
CAT NO
HR2-651
NAME
DESCRIPTION
1 gram
PRICE
$29.00
CAT NO
HR2-801
NAME
DESCRIPTION
10 grams
PRICE
$165.00
Support Material(s)
 HR2-651 HR2-801 TCEP HCl User Guide
HR2-651 HR2-801 TCEP HCl User Guide HR2-651 TCEP hydrochloride SDS
HR2-651 TCEP hydrochloride SDS HR2-801 TCEP hydrochloride SDS
HR2-801 TCEP hydrochloride SDSCertificate Of Analysis
References
1. Tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine stabilization of RNA: comparison with dithiothreitol for use with nucleic acid and thiophosphoryl chemistry. Rhee SS, Burke DH. Anal Biochem 325, 137-43 (2004) PN51541.
2. A comparison between the sulfhydryl reductants tris(2-carboxyethyl)phosphine and dithiothreitol for use in protein biochemistry. Getz EB, Xiao M, Chakrabarty T, Cooke R, Selvin PR. Anal Biochem 273, 73-80 (1999) PN34481.
3. Burns, J.A., et al. (1991). Selective reduction of disulfides by tris-(2-carboxyethyl)-phosphine. J. Org. Chem. 56, 2648-2650.
4. Oda , Y., et al. (2001). Nature Biotech19, 379-382.
